Enhancing the security of encrypted containers using VeraCrypt.
Design and implementation of a mechanism for encrypting and decrypting an additional keyfile directly on a PKCS#11 card containing a security certificate in order to leverage the cryptographic functionalities provided by this type of smart card.

This project is based on an open source software: VeraCrypt.
Available on all three major operating systems (Windows, Linux and Mac OS), VeraCrypt enables users to create encrypted, concealable virtual storage volumes. It is also possible to do the same with entire partitions.
VeraCrypt is the successor to a fork of the TrueCrypt software. It has been developed since 2014 by IDRIX, a company headed by Mounir Idrassi. External contributors are also involved in the software's development.
Since June 2013, VeraCrypt has been downloaded several million times, establishing its reputation as a leading data protection tool. Its adoption is so significant that it has been recommended by Reporters Sans Frontières in their 2021 Source Protection Guide. In addition, the Agence Nationale de la Sécurité des Systèmes d'Information ( ANSSI) recommends the use of VeraCrypt, and it was included in the Socle Interministériel des Logiciels Libres in 2018, forming part of the catalog managed by DINUM.
The VeraCrypt source code has undergone two security audits. In 2016, Quarkslab, a French company specializing in software protection and analysis, carried out the first audit. The second audit took place in 2020, conducted by the Fraunhofer Institute for Secure Information Technology on behalf of Germany's Federal Office for Information Security (BSI).
The main aim of the project is to add a new functionality to the VeraCrypt software. Until now, VeraCrypt has allowed users to use keyfiles to strengthen the entropy of their passwords. Keyfiles are files of any type that can be used to encrypt a volume, and are required for decryption if necessary. They can be stored on any physical medium, including PKCS#11 cards.
It is currently possible to use PKCS#11 smart cards, but only as a storage medium. To fully exploit the card's capacity, its cryptographic function will be used to participate in keyfile encryption and decryption. This feature will be particularly useful in the corporate environment.
This new feature enhances the encryption security of a VeraCrypt volume. Currently, when a PKCS#11 card is used to store a keyfile, users can use the same keyfile for different containers. Using the card's cryptographic capability ensures that each container has a different "key" (which may be a composition of several passwords/keyfiles).
1.1 General reminder
The aim of the solution is to enable users to strengthen the security of their containers encrypted with VeraCrypt. One possibility is to encrypt and decrypt an additional keyfile
decrypt an additional keyfile directly on the PKCS#11 card containing a security certificate
to take advantage of the cryptographic features provided by this type of smart card.
smart cards.
Some key terms:
- « master key » is the key used to decrypt container data.
- « header key » is the key used to decrypt the header.
- « header » designates the 512 bytes of a volume's header, including the master key.
- « encrypted keyfile field »field, which will be referred to as the KC field, designates the location in the header where the new encrypted keyfile will be stored.
- Le OAEP formatting (Optimal Asymmetric Encryption Padding) is a formatter for asymmetric
asymmetric encryption, and is recommended for RSA encryption by the
NIST [ 7 ]. This formatting, which is widely used on PKCS#11 cards, increases
the length of the plaintext: after RSA encryption, the ciphertext is longer than the plaintext.
plaintext. This formatting is used on the user's card.
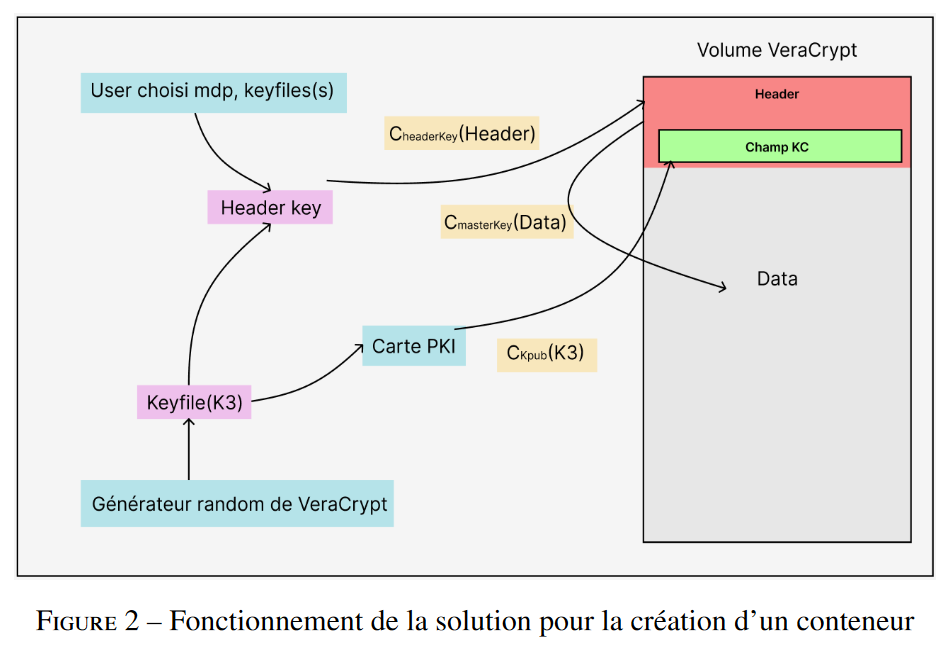
1.2 Volume creation
An encrypted volume is created using a 64-byte keyfile generated pseudorandomly with the secure random number generator included in VeraCrypt.
The container data is encrypted using the master key generated by VeraCrypt and present in the header.
Then, the header key is generated with the combination function mixing the potential passwords, the selected keyfiles as well as the newly generated keyfile. This key is used to encrypt the header.
The contents of the KC field are then sent in clear text to the PKCS#11 card, which encrypts them with the public key (Kpub) selected by the user. This variable-size cipher (between 256 and 512 bytes) will be stored in the KC field.
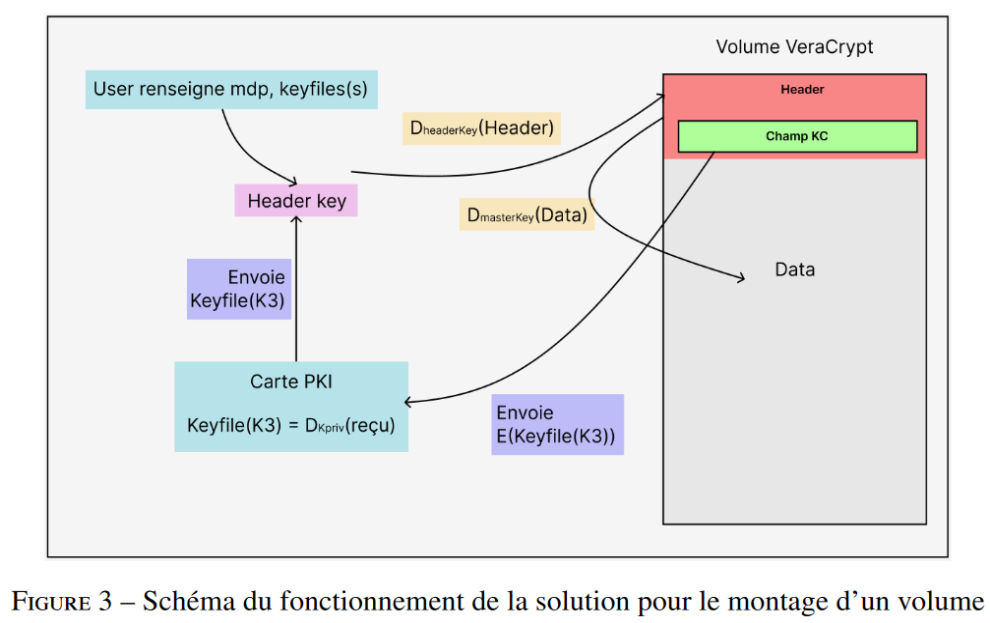
1.3 Mounting a volume
The encrypted keyfile in the KC field is sent to the PKCS#11 card, which will decrypt it using the Kpriv private key. The keyfile is sent back to VeraCrypt. Subsequently, the header will be decrypted with the key generated by combining the potential passwords and keyfiles, possibly including that of the KC field.
.
Finally, the container data can be decrypted with the master key present in the header. With this system, the keyfile will never be stored in cleartext, but will only allow access to the container once it has been decrypted.
Our team is made up of 7 students in their 4th year at the INSA Rennes computer science department:
- Malvin CHEVALLIER
- Jean HAUROGNE
- Axel HOMERY
- Antoine MARCHAL DOMBRAT
- Guillaume MERCHEZ
- Simon PORTIER
- Adrienne RESSY
This academic project, running from 2023 to 2024, is supervised by Gildas AVOINE and Mounir IDRASSI.
All of this project's output is distributed across dedicated repositories in the team's Github organization.
VeraCrypt_PKCS11 is a fork of the VeraCrypt source code, modified on the "dev" branch to add our functionality.
POC PKCS11_VeraCrypt contains a Python proof-of-concept for extracting PKCS#11 smartcard certificates and data.
WebPage corresponds to the source code of the page you are currently reading.




