What is VeraCrypt ?
This project is based on an open source cybersecurity software :
VeraCrypt.
Available for Windows, Linux and macOS, VeraCrypt allows its users
to create
encrypted virtual storage volumes hideable or even
encrypt partitions of the operating system on which it is installed.
VeraCrypt is the successor to TrueCrypt software and has been
developed since mid 2013 by
IDRIX, a company headed by
Mounir Idrassi. External contributors are also involved in the
development of the software.
Downloaded several million times since June 2013, VeraCrypt is a
reference in the field of
data protection. It has been included by
Reporters Without Borders in its
2021 Source Protection Guide. Recommended by the
ANSSI, VeraCrypt was also
included in the
Socle Interministériel des Logiciels Libres
, a catalog managed by
DINUM, in 2018.
The security of the VeraCrypt source code has been
audited twice : a first time in 2016 by
Quarkslab, a French company
specialized in software protection and analysis, and again in 2020
by the
Fraunhofer Institute for Secure Information Technology
on behalf of the
Federal Office for Information Security (BSI)
of Germany.
What is the goal ?
Currently, the security of VeraCrypt's encryption is based on the
use of a password known only to the owner of the volume. The latter
also has the possibility to use one or more additional files to
reinforce the entropy of his password : the
keyfiles. These files, integrated in the
cryptographic process of VeraCrypt, can be considered as a double
authentication factor.
Keyfiles can be stored on any media, it is possible to use a
removable memory such as a USB key for example. VeraCrypt also
allows its users to store their keyfiles on a smart card compliant
with the PKCS#11 standard, an API defining a
generic interface for cryptographic devices.
However, this approach of storing keyfiles on a PKCS#11 card,
although the most secure, is dedicated to users with minimal
cybersecurity skills. Moreover, it drastically reduces the
plausible deniability of the user. The presence of
a PCKS#11 card in a reporter's wallet may attract the attention and
suspicion of authorities when passing through customs in a hostile
state.
An alternative to the above mentioned approach is the use of smart
cards compliant with the EMV standard. These
payment cards are widely used all over the world without any
connection to the encryption of virtual volumes. Together with the
passport, these are certainly the two most widely used devices on
the globe and standardized by international standards. Almost all
VeraCrypt users have at least one EMV card.
Using the internal data of the volume creator's EMV
card as keyfiles is therefore a way to set up his double
authentication.
How to reach it ?
Project philosophy
Throughout this project, changes were made to the source code of an
existing application. We had to make sure that no security breaches
were introduced, that the code produced was naturally integrated
into the existing code, that the modifications were minimal in order
to facilitate the re-reading by other developers and finally that
the interface remained substantially the same so that the user
wouldn't be not too disturbed by these changes.
Technically, this project is divided into two steps : understanding
how EMV cards work and modifying the VeraCrypt source code to add
this functionality.
Study of EMV cards
According to the ISO/IEC 7816 standard on which the EMV standard for
contact communication is based, the dialogue with the smart card is
carried out with the help of APDU commands, the
structure of which contains numerous parameters that make it
possible to specify which information to extract.
The EMVExtractor module was therefore designed to
ensure communication between VeraCrypt and the EMV card through the
user's card reader. To cope with the diversity of readers on the
market, Microsoft has developed the Personal Computer/Smart Card
communication standard. The choice was made to use the Winscard
library, which follows this standard and is available natively under
Windows, but also under Linux or macOS via the PCSCLite package.
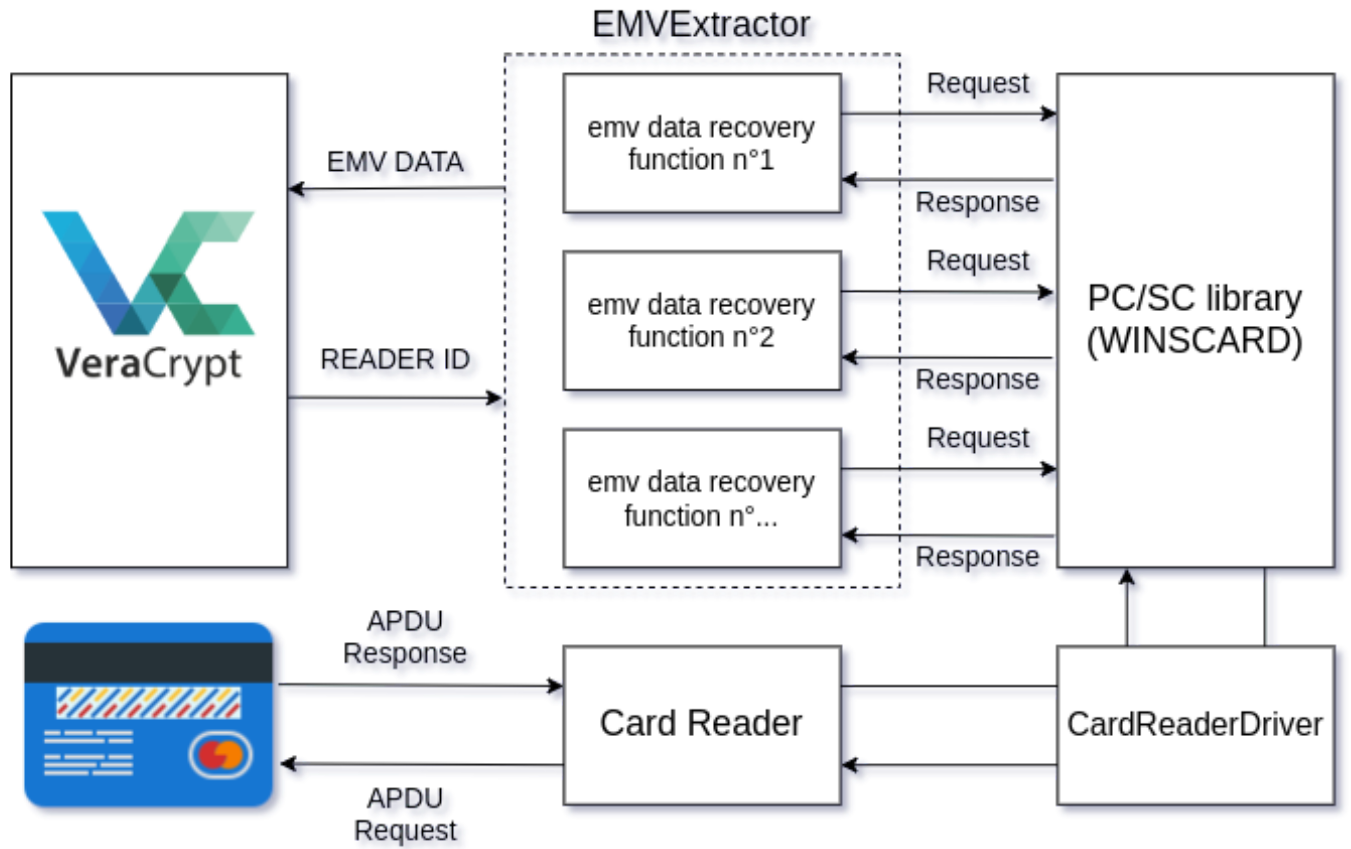
Concerning the data to be extracted from the EMV card to be used as
keyfiles, the ICC Public Key Certificate and
ISSUER Public Key Certificate as well as the
Card Production Life Cycle data have been retained
because they are unique to the card.
Modification of VeraCrypt
The implementation for EMV cards is inspired by the one developed
for the use of PKCS#11 cards in VeraCrypt. The window for selecting
keyfiles on smart cards has been reused : a template dedicated to
EMV cards has been added. The last four digits of the connected EMV
card numbers are displayed for selection.
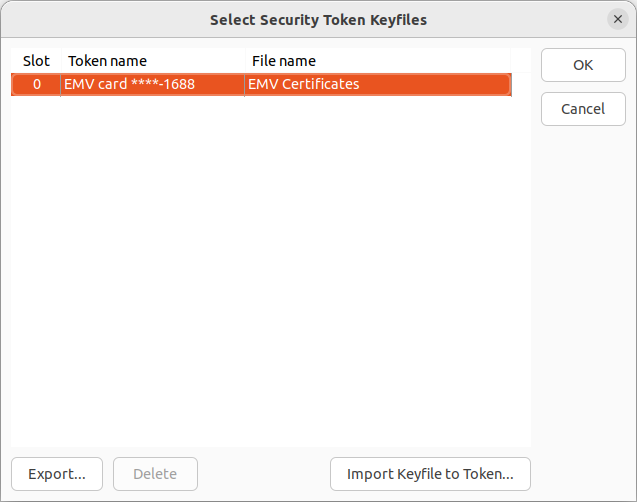
Since EMV cards are read-only, some features such as data deletion
(Delete button) have been disabled.
In general, cybersecurity software users like to be in full control
of the application's functionality. Thus, the EMV functionality is
optional and disabled by default in the software
settings.
Who are we ?

Our team is composed of 7 students in 4th year in the computer
science department of INSA Rennes :
This academic project, carried out over the year 2022-2023, is
supervised by Gildas AVOINE and Jules DUPAS.
Take a glance ?
The entire production of this project is distributed in the
dedicated repositories of the team's
Github organization
.
-
VeraCrypt_EMV
is a fork of the VeraCrypt source code, modified on the
dev branch to add the EMV functionality.
-
EMV_Extractor
contains a python POC and its C++ translation to extract
certificates and data from EMV smart cards.
-
Web_page
is the source code of the page you are currently viewing.
-
Reports
stores PDF versions of reports written throughout the different
phases of the project (in French only).


